What is RPA?
In simple terms, Robotic Process Automation is a software that can perform high volume and repetitive tasks just as humans do. For example, creating invoices by collecting data and mailing them to the relevant persons.
RPA software is based on artificial intelligence and machine learning. The software is programmed in such a way that it follows a basic algorithm and deliver the required results. They are designed just to mimic a human worker. These software/robots can also perform complex tasks.
RPA can be classified into three main categories,
1.Probots - These types of Robots can perform simple repetitive tasks.
2.Knowbots - It is used to gather and store information and then analyze it.
3.Chatbots - It simulates human conversation through voice or text. Sometimes it is so accurate that it becomes difficult to differentiate between customer service executive and a chatbot.
Benefits and Features of RPA
- Improved Efficiency: RPA can automate tasks that are time-consuming and error-prone, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic work. For example, a bot can automatically process invoices, reducing the time it takes to pay suppliers.
- Reduced Costs: RPA can help businesses reduce costs by eliminating the need for manual labor and reducing errors. For example, a bot can reduce the number of errors made when entering data, saving the company money on rework.
- Process Automation: RPA can perform any repetitive, rule-driven task that involves structured data. For instance, a software robot can automatically input data into a spreadsheet.
- Increased Accuracy: RPA can improve accuracy by eliminating human error from tasks. For example, a bot can accurately process orders without making mistakes that humans might make.
- Integration: RPA can be integrated with existing systems and applications. For example, a bot can be integrated with a customer relationship management (CRM) system to automatically update customer records.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: RPA can help businesses improve customer satisfaction by providing faster and more accurate service. For example, a bot can answer customer inquiries 24/7, reducing wait times.
- Scalability: RPA can be easily modified to adapt to changes in business needs. For example, a company can add more bots to handle increased workload during peak times.
- Security: RPA can be used to improve security by automating tasks that are vulnerable to human error. For example, a bot can automatically log users out of systems after a period of inactivity, reducing the risk of unauthorized access
Downsides Of RPA
- Limited Flexibility and Scalability: RPA is designed to automate structured, rule-based tasks. It struggles to handle unstructured data, complex decision-making, and dynamic processes. As businesses evolve and face changing requirements, RPA may become less effective. Moreover, scaling RPA solutions can be challenging. As the volume of work increases, RPA may not be able to keep up, leading to bottlenecks and delays. In such cases, businesses must consider Scale alternatives to avoid these issues.
- Dependency on Human Intervention: Although robotic process automation (RPA) can perform numerous tasks automatically, it frequently necessitates human involvement to address exceptions, errors, and intricate scenarios. This can limit the extent of automation and increase operational costs. For example, if an RPA bot encounters an unexpected error, a human operator may need to intervene to resolve the issue. This can slow down the process and reduce the overall benefits of automation.
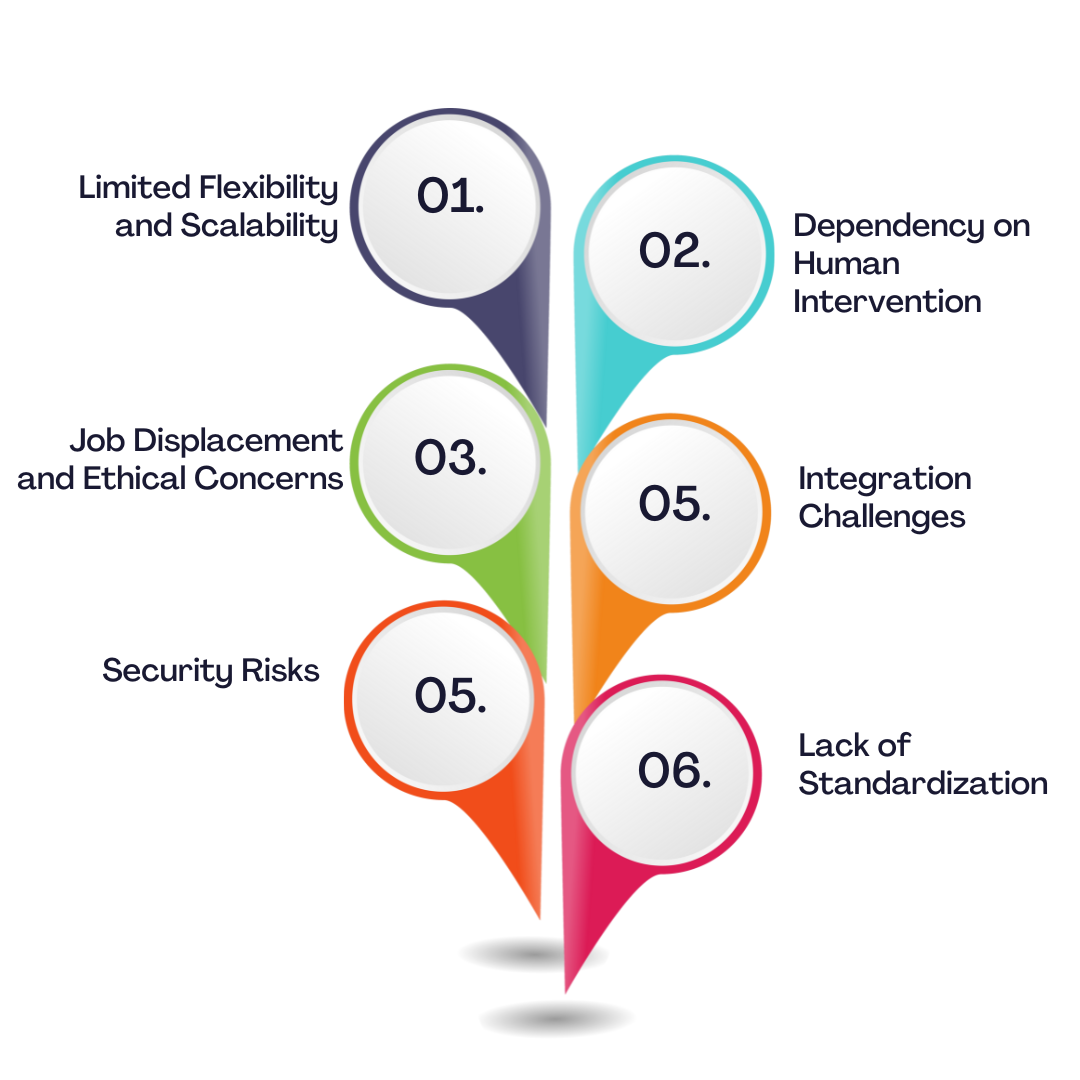
- Job Displacement and Ethical Concerns: The widespread adoption of RPA raises concerns about job displacement. As automation becomes more prevalent, there is a risk that certain roles may become obsolete. This can lead to social and economic challenges. Additionally, the use of RPA raises ethical questions. For example, there may be concerns about the impact of automation on data privacy and security.
- Integration Challenges: Incorporating RPA into existing systems and applications can be intricate and time-intensive. This can hinder the implementation process and raise associated expenses. Moreover, ensuring compatibility between RPA tools and other systems can be challenging, especially in heterogeneous IT environments.
- Security Risks: RPA can introduce new security risks if not implemented and managed properly. For example, unauthorized access to RPA bots could lead to data breaches or disruptions to business operations. It is essential to implement robust security measures to protect RPA systems and prevent unauthorized access.
- Lack of Standardization: The RPA market is still relatively new, and there is a lack of standardization in terms of tools, processes, and best practices. This can make it challenging to compare different RPA solutions and implement them effectively. The lack of standardization can also lead to increased complexity and costs.
Applications Of Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is transforming how businesses operate across various sectors. Here's a breakdown of how RPA streamlines tasks in different industries:
1. Travel and Logistics: Imagine passengers booking flights and receiving confirmation emails automatically, thanks to RPA bots handling the ticketing process. This saves time for both travelers and customer service representatives.
2. Healthcare: RPA can automate patient record management and claims processing, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on providing better patient care.
3. Human Resources (HR): Say goodbye to manual candidate shortlisting. RPA can scan resumes and shortlist qualified applicants based on pre-defined criteria. Additionally, employee details like salaries, leave requests, and email updates can be managed automatically.
4. Customer Service: Chatbots powered by RPA can handle basic customer inquiries around the clock, improving customer satisfaction and reducing wait times. Verifying information, sending automated sales emails, and handling billing can also be automated, making customer service more efficient.
5. Supply Chain Management: Order details, package tracking, and inventory management can be seamlessly automated using RPA. This ensures accurate inventory levels and reduces the risk of stockouts. Additionally, processing orders, payments, and data management can be streamlined.
6. Banking and Finance: From automated account opening and closing to managing foreign exchange and card activation, RPA can significantly accelerate banking processes. Furthermore, RPA can streamline insurance claims processing, sending customer messages, online transaction processing, and managing funds.
7. Big Data Processing and Data Mining: RPA can be used to manage, secure, and store vast amounts of data efficiently. By automating data wrangling and cleansing tasks, RPA helps businesses extract valuable insights from their data.
The Future Of RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is becoming a significant technological advancement in the 21st century. Although it's still in its early stages, we can expect substantial improvements in the future. According to a Forrester report, the RPA market is projected to exceed $20 billion by 2024.
- Different industries like manufacturing, aviation, retail, etc. will be using RPA.
- Data entry and Data mining jobs will soon become extinct
- It will be used to give more accurate results and improve efficiency
Artificial Intelligence combined with RPA will improve the algorithm and will be able to perform operations with logic.
In the future, RPA will likely make our lives easier by automating more jobs. Workers may no longer have to perform repetitive and mundane tasks. Research from Oxford University suggests that 40% of jobs could be automated by RPA. This shift can drive up efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
The next generation of RPA, often referred to as RPA 2.0, will incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence technologies. This will enable unassisted RPA to perform operations without human interaction. However, clear algorithms and rules must be defined for the software to function effectively.
Future Trends of RPA
1. Hyperautomation: Beyond RPA
Hyperautomation goes beyond traditional RPA by integrating various technologies to automate complex processes. This includes artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and intelligent process automation (IPA). By combining these technologies, businesses can achieve end-to-end automation, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
For example, a company can use hyperautomation to automate a complex process like order fulfillment. AI can be used to predict demand, ML can be used to optimize inventory levels, and RPA can be used to automate tasks like order processing and shipping. To further streamline operations, some businesses also explore Zapier competitors that offer advanced automation capabilities with different integrations and features.
2. Intelligent Process Automation (IPA): Infusing RPA with AI
IPA combines RPA with AI and ML to create more intelligent and adaptable automation solutions. By incorporating cognitive capabilities, IPA can handle unstructured data, make decisions, and learn from experiences. Robotic Process Automation can now tackle more sophisticated tasks and adjust to evolving business needs.
For instance, an insurance company can use IPA to automate the process of assessing claims. AI can be used to analyze documents and identify potential fraud, while RPA can be used to process legitimate claims.
3. RPA as a Service (RaaS): A Flexible Deployment Model
RaaS is a cloud-based delivery model that allows businesses to access RPA capabilities on a subscription basis. This eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and software, making RPA more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
By using RaaS, businesses can quickly deploy RPA solutions without the need for extensive IT resources. This can help them accelerate their digital transformation initiatives and realize the benefits of automation sooner.
4. RPA for Customer Experience (CX): Enhancing Customer Interactions
RPA can be used to improve customer experiences by automating tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, and error-prone. This can result in quicker reactions, less waiting, and happier customers.
For example, a bank can use RPA to automate the process of opening new accounts. This can reduce the time it takes for customers to open accounts and improve their overall experience.
5. RPA and Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Democratizing Automation
Low-code/no-code platforms make it easier for non-technical users to develop RPA solutions. These platforms provide a visual interface that allows users to drag and drop components to create automation workflows.
This democratization of RPA enables a wider range of employees to contribute to automation initiatives. This can lead to increased innovation and faster time-to-value.
Why RPA is Right for Your Company?
If your company processes insurance claims, RPA can be a valuable tool. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA can help you improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase accuracy.Here are some specific examples of how RPA can benefit a company that processes insurance claims:
- Faster claim processing: RPA can automate the process of reviewing claims for accuracy, reducing the time it takes to process each claim. This can improve customer satisfaction and help you meet regulatory deadlines.
- Reduced errors: RPA can help reduce the number of errors made when processing claims. This can save your company money on rework and improve the accuracy of your data.
- Improved compliance: RPA can help you comply with regulatory requirements by automating tasks such as data entry and reporting.
- Increased efficiency: RPA can allow your employees to concentrate on more important responsibilities, such as analyzing complex claims.
- Reduced costs: RPA can help you reduce costs by eliminating the need for manual labor and reducing errors.
To learn more about how RPA can benefit your specific business processes and streamline your operations, consider hiring an RPA developer. They can assess your needs, identify potential automation opportunities, and implement RPA solutions tailored to your company's requirements.


.webp?lang=en-US&ext=.webp)

.webp?lang=en-US&ext=.webp)

